Working-, Doing- or Learning-Environments
Designing Dynamical Learning Environments for Simulation: Micro-Worlds & Applets on the World Wide Web
Dr. ir. Rik Min
researcher / designer
Ir. Jan de Goeijen
developer / software engineer
Faculty of Educational Science and Technology (EDTE), University of Twente (UT)
Postbus 217; 7500 AE Enschede, The Netherlands. E-mail: Min@edte.utwente.nl
http://users.edte.utwente.nl/min
Abstract
A student today no longer spends his time in a lonely little attic room, a noisy lecture room or the deadly silence in the huge reading room of a university library. These components of his environment still exist but their functionality has changed. In principal all students at the campus of the University of Twente (UT) have an excellent connection with the electronic highway. The World Wide Web is extremely popular, both among lecturers and students. It fills the almost natural need of young people to want to travel all over the world and to try and understand it. All this at minimum cost please.
For many courses, e-mailing with the lecturer is a matter of course. So is publishing educational material on the Web. At our university we teach students in their 2nd, 3rd and 4th year, to make eductional IT applications (in java and javascript) and to implement them in (normal) courseware or instruction programs. The courseware so become - what we called - higher order courseware. Our students have to learn designing and developing Learning- and Instruction-environments with intelligent modules. We combine the design-courses with our research & development-projects. This projects do research to modern, multimedial learning environments based on special designed simulations and a new design-theory: the 'Parallel Instruction' theory for web-based simulations.
Pilot projects
During the past academic year we have conducted pilot studies into the possibilities and the 'performance' (i.e. the 'strength' or the 'power') of HTML, javascript and Java: the 'WebLib'-project and the 'SimLib'-project. In particular for on-line learning environments for simulation and problem solving in front of a computer monitor. A number of different interactive on-line examples have been developed and a number of different on-line tests have been created. This research has let to educational applications.
Projects
- SimLib-project
- WebLib-project
- ICS-project
- PI-theory-project
- JavaTHESIS-project
Topics
- Web-based Materials
- Model-driven Simulations
- Parallel Instruction theory (an design theory: the PI theory)
- Parallelism as Concept and Design Phenomena
- Open Learning Environments (with parallel instructions)
- Embedded Simulation Environments
- E-Learning
- Interactive Scientific Papers (ISP)
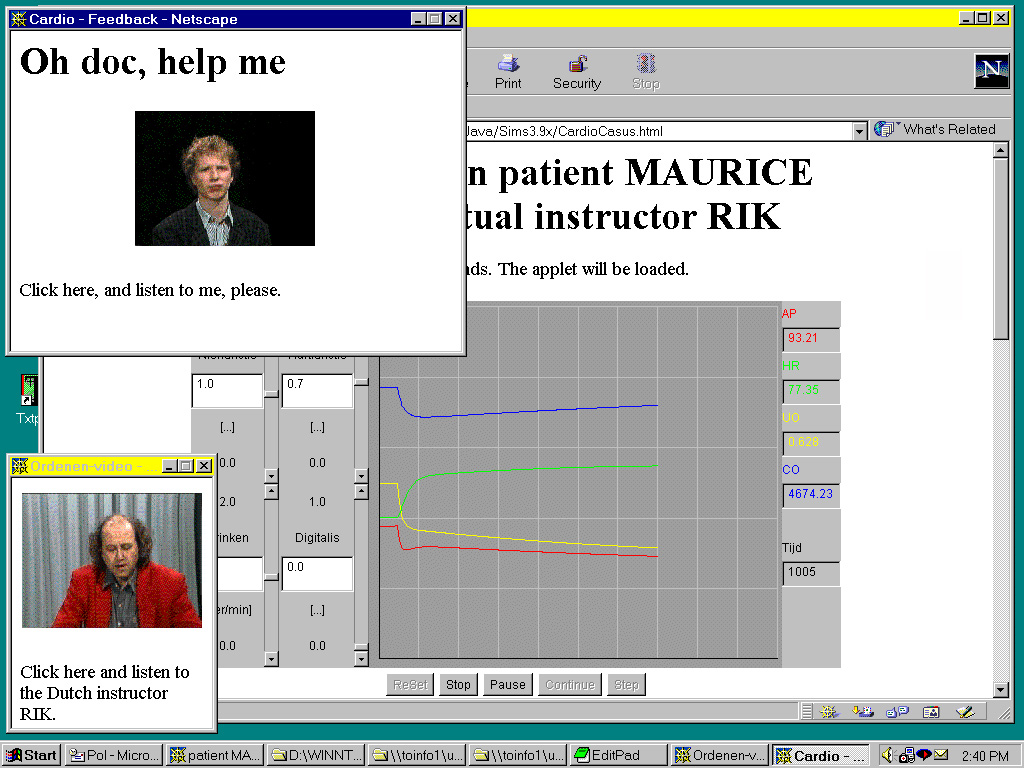
Screendump 1. Simulation site with CARDIO; built with 'SimLib' and JavaTHESIS.
Methods & Techniques
- Applets as building blocks
- Java and Javascript templetes (shells)
- Libraries: WebLib and SimLib
- E-Learning and Web-Based Training (WBT)
- Intelligent feedback (ICS)
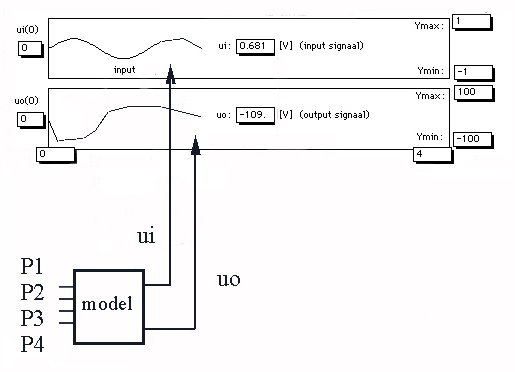
Principle of model-driven simulations
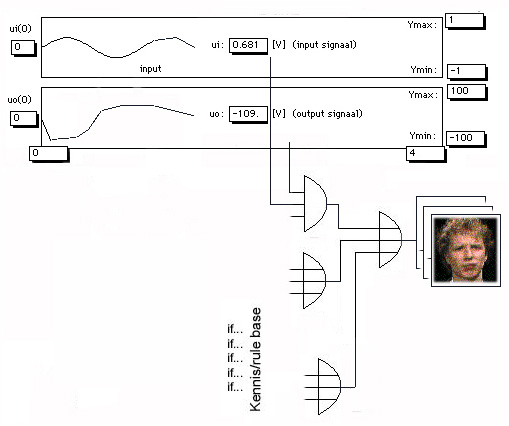
Principle of intelligent feedback: here video fragments
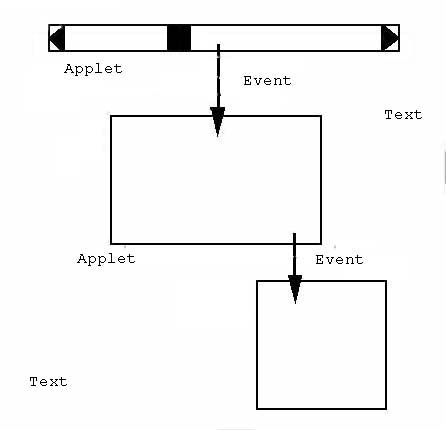
Principle of building blocks with events between input-applets and output-applets

Screendump 2. Simulation site with CARDIO; built with 'WebLib' and javascript.
Parallel instruction
type 1 order parallelism:

left: the open doing environment; right: the instruction (scrollable)
Parallel instruction
type 2 order parallelism (a):

left: worksheet with applet; right: instruction
Parallel instruction
type 2 order parallelism (b):

left: applet; right: home-base with instruction etc.
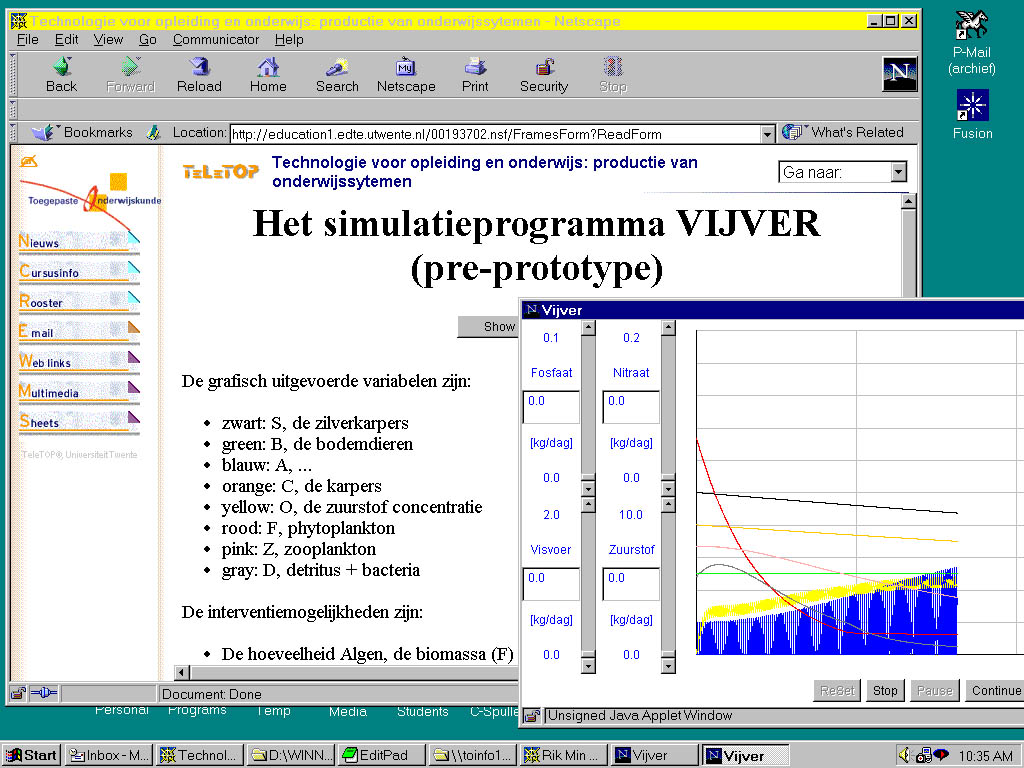
Screendump 3. Simulation site with FISH POND; built with 'SimLib' and JavaTHESIS (embedded in TeleTOP)
Simulators
- The phenomena of the Cardiovascular System (2 versions)
- The phenomena of the Water and Salt regulation in the human body
- The phenomena of the Dutch Economy
- The phenomena of an Sun heater
- The phenomena of an Transistor
- The phenomena of Resistances and Capacitors (RC-networks - Filters)
- The phenomena of an Fishing Pond
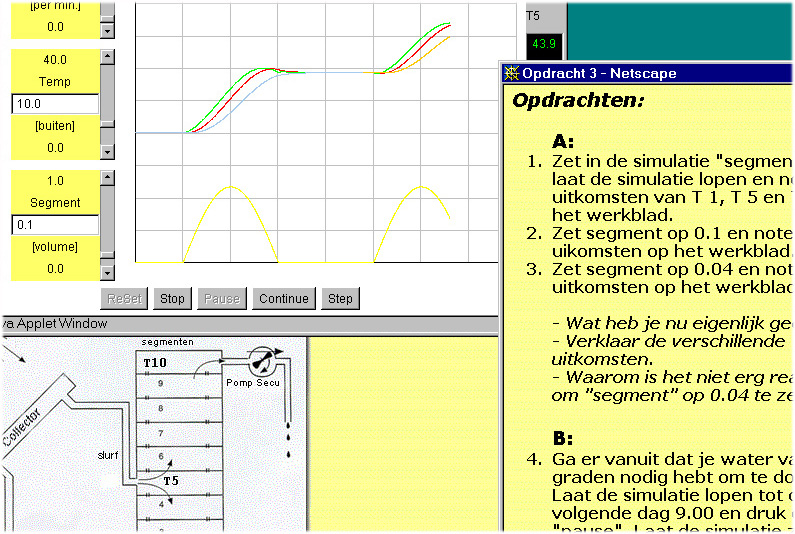
Screendump 4. Simulation site with BOILER; built with 'SimLib' and JavaTHESIS
Conclusions
- Built your own Libraries (as WebLib and SimLib)
- Connect Applets with Applets
- Connect Input Applets with Output Applets (with events)
- Use JavaScript and 'WebLib' with Building Blocks
- Use Java and 'SimLib' for model-driven Simulations
- Use JavaTHESIS (Min, Sikken, de Goeijen; 1997 - 2001)
- Use templates or shells (as in JavaTHESIS and WebLib)
== more about parallellism and the PI theory ==
== parallellism
and the PI theory ==
Enschede: Tampere, june 29 & Fribourg, aug 30, 2001.








