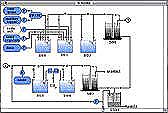
FLUIDS
Thisis a simulation program of the effects of lack of water and electrolites on a human body. Students can add fluids to the body. The mathematical model underlying this program contains over 200 variables and describes control mechanisms of body fluid volumes and electrolytes as well as respiratory control mechanisms. This model
allows a variety of simulations of e.g. thirst, fluid loss,
exaggerated drinking, carbon dioxide inhalation, severe physical
exercise, etc. The student can again infuse fluids of different
compositions, give a diuretic, etc. The basic physiology of respiratory and
metabolic acidosis and alkalosis can be studied with this model. It is based
an a model developed by Ikeda et al, Japan.
The computer simulation program FLUIDS enables students to experiment with a model of the human water and electrolyte system and the regulation of
respiration and its underlying (basic) physiology and pathophysiology. The
simulation consists of the following: heart and cardiovascular system,
lungs, intra- and extra cellular fluid compartments, nerve reflections, the
kidney, and a number of hormonal systems with an influence on the kidney
function. In some ways this simulation coincides with the model of the
computer simulation program CARDIO, but in several important parts it is
much more extensive. The computer simulation program FLUIDS simulates a kind of experimental laboratory environment, so that students can do research on
water and salt regulation and the regulation of respiration under various
circumstances.

AORTA (Mac and web versions)
In early phase of their studies medical students can familiarize themselves with some basic concepts from hemodynamics and some aspects of arteriosclerosis. In using this program an answer is given to questions like:
'What happens if the total peripheral resistance of the circulation is increased?'
The opposite can also be an educational goal, namely the question as to what is the cause of the deviating picture of the diastolic pressure in the aorta. 'Can the cause of a decreased diastolic pressure in the aorta be a decreased compliance of the aorta? Yes or no?'
Students learn to handle notions like compliance and total peripheral resistance and changes there in. Students are supposed to be able to formulate questions and/or hypotheses and to verify these hypotheses with the help of this simulation program. Within the framework of a course about arteriosclerosis, case studies has been developed about the hardening of the wall of the aorta and the increased total resistance of the peripheral circulation. In this case study the students themselves have to recognize that the mean peripheral stream has changed and they have to try to restore it by adapting the pressure of the ventricle. The program is intended to teach the students how to deal with basal hemodynamic relations such as between pressure, compliance and volume and those between stream, resistance and pressure and to determine the consequences of interventions in hemodynamic variables.
The aorta is the great artery which springs from the left ventricle in the heart. The heart pumps (with a certain pressure) a quantity of blood through the human body with each heart beat attended by a change in pressure in the aorta. The aorta itself is elastic. The quantity which plays a role in the elasticity of the aorta is compliance. There is a connection between the form of the changes in pressure in the aorta and compliance. Furthermore there is a connection between the blood pressure in the aorta, the quantity of blood which flows through the aorta and the resistance offered by the body (the peripheral resistance). The interesting variable to be measured externally, 'the pulse pressure', is practically equal to the pressure of the aorta. This pressure varies considerably and is very characteristic.
CELLS
This program simulates the growth of two kinds of single-celled organisms in
laboratory cultures. The organisms compete with one another over limited
resources. This model is from Lotka, A.J. (1925). Elements of physical
biology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore. (Reprtinted as: Elements of
mathematical biology in1956 by Dover, New York). A more modern treatment can
be found in: Pianka, E.R. (1978). Evolutionary Ecology. Harper & Row. New
York. The application contains five cases: competitive exclusion, stable equilibrium, symbiosis, fragile equilibrium and a steady state simulation about a monoculture of species 1.
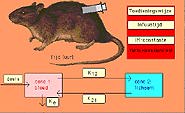
FARMA (Mac and web versions)
This program is a simulation of the two-compartiments model from
farmacokinetics. The program is exclusively meant for demonstration
purposes. The program have three ways of administering drugs: intravenous, infusion and intra-muscular.
Others:
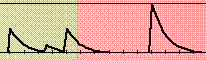
GLUCOSE
This program is based on a model of the insuline and glucose mechanismes in the human body. It is a product of the University of Twente in cooporation with the University of Leiden (RUL) (Toegepaste Biologie) (1993). You see the influence of eating in the morning, the lunch and the diner; plus in the morning some cookies.

AXON (Mac and web versions)
More than fifty years ago action potentials were first recorded by means of
external electrodes by Hodgkin and Huxley. Based on the results of their
experiments they designed a new revolutionary theory about action potential
generation which meant a breakthrough in electrophysiology at the time. In
1952 Hodgkin and Huxley published a quantitative model of the electrical and
electrochemical phenomena in the environment of the membrane of a nerve
fiber based on their theory. The original model of Hodgkin and Huxley was
not a mathematical model but an electric circuit consisting of capacitors
and resistors. however, it is very simple to transfer this model into a
mathematical model.
The prototype AXON is based on such a mathematical
model. Although some of the aspects of the conductivity of the cell membrane
were not described correctly by Hodgkin and Huxley, their model is still
very useful for the education of medical students and biology students as it
can be used as a simplified version of the correct model thus helping the
students to build a conceptual 'framework' model which can be filled with
the complete and correct conceptual model in a later phase of their
education. It can also be used as a demonstration for the experimental
research techniques used in cell physiology.
Ecological stuff:
(made for biology class secondary school)

LEMMINGEN (Mac and web versions)
This program is a simulation program of how pray and hunter can influence
each others lives. It contains a prey-beast /predator model. The program is a
simulation of a small tundra ecosystem consisting of lemmings, foxes, and
grass. It is based on a model developed by P. van Schaick Zillesen.
On the arctic tundra strong fluctuations occur in the numbers of lemming,
predators and herbs. At the end of years with extremely high densities
(outbreaks) of lemmings all the plants are eaten causing starvation of most
of the lemmings. Years with outbreaks of lemming are usually followed by
years with extremely low densities.
After an outbreak of lemmings it will usually take three or four years
before the next outbreak occurs. Fluctuations of predators like arctic
foxes, which are dependent on lemmings as their main source of food, usually
show the same pattern as the lemming fluctuations (with some delay).
Schultz (1969) described the relations between lemmings, their food (herbs),
their predators (mainly arctic foxes) and the bottom of the arctic tundra.
He emphasized the role of changing nutrient concentrations in the dynamics
of the arctic tundra system. In the spring of a year with an outbreak of
lemmings almost all minerals are present in the herbs. However, as a result
of the consumption by the rodents most of these nutrients are deposited on
the surface of the tundra in the form of faeces during the same year. The
next year plant growth is minimal because of the low nutrient concentrations
prevailing in the soil. It will take several years for the faeces to
mineralize because of the extreme polar climate. However, the third year
after the outbreak the mineral level of the tundra soil has gradually
increased to a point that enables rapid plant growth. However, the nutrient
level in the crop is still very low during this year. A high nutrient level
in the crop, enabling a good lactation in lemming females, is required in
order to cause a lemming breeding success. For this reason the number of
lemmings does not rise proportionally to the plant growth during this year.
However, during the next year the nutrient concentration in the herbs is
much higher causing a new outbreak of lemmings. The program LEMMING
simulates the processes described above. The model on which the program is
based has been developed as part of this study and has so far not been
published anywhere else.
FOOD CHAIN / VIJVER (Mac and web versions)
Fish ponds are widely used by man for food production. The management of a .i.fish pond; affects the entire ecosystem, including fish, nutrients, zooplankton, benthos, dissolved oxygen, microorganisms etc. A high efficiency of fish breeding can be achieved only with optimum values of the control parameters of the pond, like the input of fertilizers, the re-aeration of the water in case of oxygen depletion and the addition of artificial fodder. Svirezhev et al. (1984) developed optimum control strategies for a fish pond ecosystem. As part of their study they constructed a mathematical model of a fish pond. Van Schaick Zillesen designed and realised the computer simulation program FOOD CHAIN (VIJVER) with a lot of instructional support (also on MS.DOS with the THESIS system) for de Stichting Leerplan ontwikkeling (SLO, National Institute for Curriculum Development) in cooporation with Hartsuiker et al. (Dutch version).
Due to the relatively simple tropic structure a fish pond can be an excellent case for the study of the characteristics of food-chains and ecosystems in general. However, fish ponds can not be studied in the biology curriculum for practical reasons (space and time). A computer simulation program, simulating a fish pond can be an excellent tool to overcome these problems.
For this reason a mathematical model of a fish pond can serve two purposes: fish pond management and education. The model constructed by Svirezhev et al (1984) simulates a fish breeding pond in which three fish species are present: carp, silver carp and bighead carp. Van Schaick Zillesen adapted the model for a pond in which only two fish species are present (carp and silver carp).
The program FOOD CHAIN is based on the adapted version of the model of Svirezhev et al. Svirezhev et al. (1984) give values the parameters used in their model. However, they do not give starting values for the variables of the model. Labordus (SLO) gathered the data about the values of these variables from literature.

SUCROS
This simulation models the growth of grain in Zambia. It is based an a research model
developed by H. van Keulen (from the University of Wageningen and connected at ITC, Enschede). It is a training program for students and pupils in argriculture.
Technical stuff:
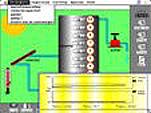
BOILER / ZONNEBOILER / SOLAR HEATER (Mac and web versions)
The computer simulation program BOILER was developed by a graduate student at the faculty of Educational Science and Technology at the University of Twente. During the development there was cooperation with staff members of the Stichting voor de Leerplanontwikkeling (Foundation for the development of curriculums) Enschede of the project Alternatieve Energie (alternative energy) in elementary vocational education. The computer program is available for Apple Macintosh and MS.DOS computers.
The computer simulation program BOILER enables students to become familiar with the characteristics of a solar boiler and to gain insight into the influences of different interventions in the model around the installation. The model simulates the working of a solar boiler installation consisting of a collector, a storage vessel, a heat exchanger with a pump which runs through the collector and storage vessel and a possibility for tapping. Intervention is possible in the model. For example, students can change the intensity of the sun-rays or the heat capacity of the collector. The students has two screen pages at their disposal. One page with a visualized representation of the underlying mathematical model of the solar boiler installation and a page graphically representing the temperature of the heated water.
The target group for the computer simulation program BOILER are students of elementary and secondary vocational education. The object is that the students increase their insight into the working of the installation and its characteristics while working with the program. That is why the students should already have some theoretical knowledge with regard to the solar boiler. So the program can best be used in e.g. a course in which theory is dealt with first. After that they are introduced to the characteristics of the installation through a real solar boiler installation. Finally the students can increase their insight into the working of the installation with the computer simulation program by experimenting with all sorts of interventions which are not possible with a real installation. Three cases have been developed in the computer simulation program BOILER with which the students can practice with the characteristics of the installation in special situations.
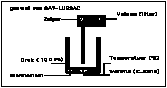
BOYLE GAY LUSSAC (Mac version only)
This program is based on the laws of thermodynamics. Simulations based on the Boyle Gay Lussac model are very illustative for students, just like this simulation application.
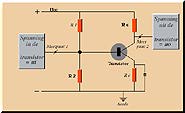
TRANSISTOR
(Mac and web versions)
Many mathematical models of a transistor are known. Some of these models are
matrix-models, treating the transistor as a black box, presenting sets of
values of output variables as a result of sets of values of input
parameters like input impedance, voltage gain etc. Other models simulate the transistor
in a more transparent way. In these models, the transistor is described by
means of an electronic circuit. The models can be used in order to study the
transistor's behaviour in a dynamic way by changing the parameters. The
model of a transistor, implemented in the prototype TRANSISTOR, belongs to
the second type of models. It describes the behaviour of a transistor in a
normal low signal amplifier circuit. The model has been developed for
educational applications by Min and Malhotra (1988) and Min and Van Leeuwen
(1990)
Mathematical stuff:
REEKSEN (Mac and web versions)
This program is based on a model from R.D. Carmichel en E.R. Smith of the Taylor equations. It is a product of the University of Twente in cooporation with the University of Delft (THD) (1985). The contents are: sinus(t), exp(t) and ln (1 + t).
CHAOS (Mac and web versions)
This program is based on a model from Lorentz: the Lorenz equations for chaos. It is a product of the University of Twente in cooporation with the University of Delft (THD). The contents are the 3 differential equations of the model of Lorentz.
INTEGRATOR (web versions)
This program is based on the integration equation. It is a product of the University of Twente for our e-books about integration (2002).
KAPITAAL (web versions)
This program is based on a conceptual model about the flow of capital. It is a product of Rik Min himself (2005).
Animation stuff:
PLC, a programmable logical controler
This program is based on the programmable environement of a PLC. It is a interactive Multimedia product with 'modelling' aspects. The most important output is an linear animation of a special industrial 'PLC-driven' robot with 9 'model-driven animation objects' (built with CAILIB). It is a simulation product of the University of Twente in cooporation with the Stichting Leerplan Ontwikkeling (SLO) te Enschede (1985) (Wolters, van Doorn and Min, 1985-1990)
PADDLE (web versions only)
This program is based on an idea from the Max Planck Institute (D). We develop this
formula-driven animation with 'eys' and 'paddles' for an illustation of an 'intelligent' animation object for our lessons and our e-books.
PLANET (web versions only)
This program is based on a simple mathematical model. We develop these
applications for an illustation of an forumula-driven animation for our lessons and our e-books.
BALL (web versions only)
This program is based on a simple mathematical model. We develop these
applications for an illustation of an forumula-driven animation for our lessons and our e-books.
Enschede, 1985 - 2012