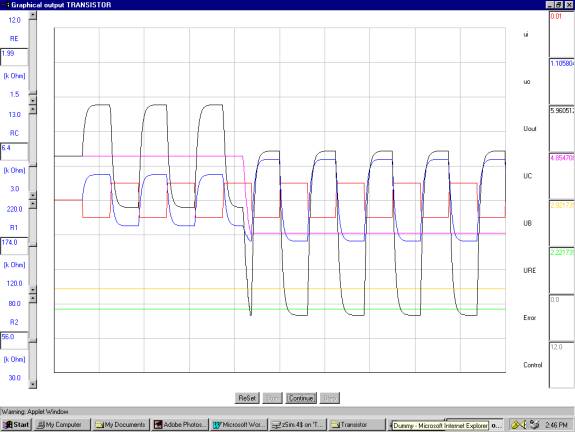
In this practice, the effects of changing the value of RC will be examined. The practice includes 2 parts:
a) increase the value of RC.
b) decrease the value of RC.
Following is the procedure for the practice, as well as analysis
of the effects of changing the value of RC.
a)
Increase the value of RC
Procedure:
1.
Click “Continue” to start the simulation
2.
After a while (e.g. when the curves are reaching the 5th
grid), pull up the scaler in the scrollbar next to “RC” to increase
the value of RC.
3.
Observe how each of the 5 curves (except the curve for ui) changes.

Analysis:
RC: increase =>
UB
= Ucc*R2/(R1+R2): unchanged
URE
= UB - 0.7: unchanged
UC
= Ucc - IC*RC: decrease
[because
IC = IRE = URE/RE: unchanged]
uo
= -40*IC0*RC*ui1: increase
[because
IC = IRE = URE/RE: decrease]
Uout
= UC + uo: decrease
[because
although uo increases at the same time UC decreases, the decreased amount of UC
is much larger than the increased amount of uo]
b)
Decrease the value of RC
Procedure:
1.
Click “Continue” to start the simulation
2.
After a while (e.g. when the curves are reaching the 5th
grid), pull down the scaler in the scrollbar next to “RC” to decrease
the value of RC.
3.
Observe how each of the 5 curves (except the curve for ui) changes.
Analysis:
RC: decrease =>
UB:
unchanged
URE:
unchanged
UC:
increase
uo:
decrease
Uout:
increase